
I remember the first time I encountered VMware Workstation, I was amused by the wizardly! I was just getting into tech and I wanted to try things out – linux in particular, but I could not risk installing it on my personal computer but then I encountered Virtualization! Finally I could run and learn Linux and break things without running the risk of wrecking my computer as a newbie. Decades later, Virtualization and VMware has evolved from a software being used on personal computers, to an entire ecosystem and market leader that major organizations run their entire IT infrastructure on. Virtualization has revolutionized the way organizations manage their IT infrastructure.
Virtualization works (not so simply) by abstracting hardware resources and creating virtual machines (VMs), that can be run on one single hardware, with it, businesses can achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Vmware is a leader in virtualization technology, and it offers a robust suite of tools to help organizations build and manage virtualized environments. In this article, we’ll explore some key components of VMware’s virtualization ecosystem—VMware ESXi, vCenter Server, and vSphere—and explain how they work together to improve hardware efficiency and streamline IT operations.
In this guide, I will walk you through the basics of setting up a virtual infrastructure with these Vmware components. Let’s dive in!
First, What is VMware Virtualization?
Before we get into the specifics of VMware’s solutions, let’s briefly discuss what virtualization is and why it’s an amazing technology. Virtualization allows you to run multiple operating systems (OS) and applications on a single physical server by creating what is literally called virtual machines (VMs). Each VM operates independently, with its own OS, applications, and resources, even though they share the same physical hardware.
The advantage of this approach is that it maximizes hardware utilization, reduces hardware costs, and simplifies IT management. VMware’s virtualization solutions have taken this idea to the next level, offering organizations enterprise-grade features for performance, security, and scalability.
Key Features/Components of note.
ESXi is the hypervisor that forms the foundation of vSphere. It’s a bare-metal hypervisor, meaning it installs directly onto the physical server without a host operating system.
vCenter Server is the centralized management platform for vSphere environments.
The vSphere Client is the user interface (UI) used to interact with vSphere.
DRS is a resource management feature that automatically balances workloads across ESXi hosts.
vMotion is a feature that allows you to migrate running VMs from one ESXi host to another without downtime
HA is a feature that ensures your VMs remain available in the event of a hardware failure.
These are some of the aspects we will touch when we start setting up our Infrastructure and test out the capabilities of our virtual infrastructure.
ESXi, vCenter and vSphere in VMware’s Virtualization Ecosystem
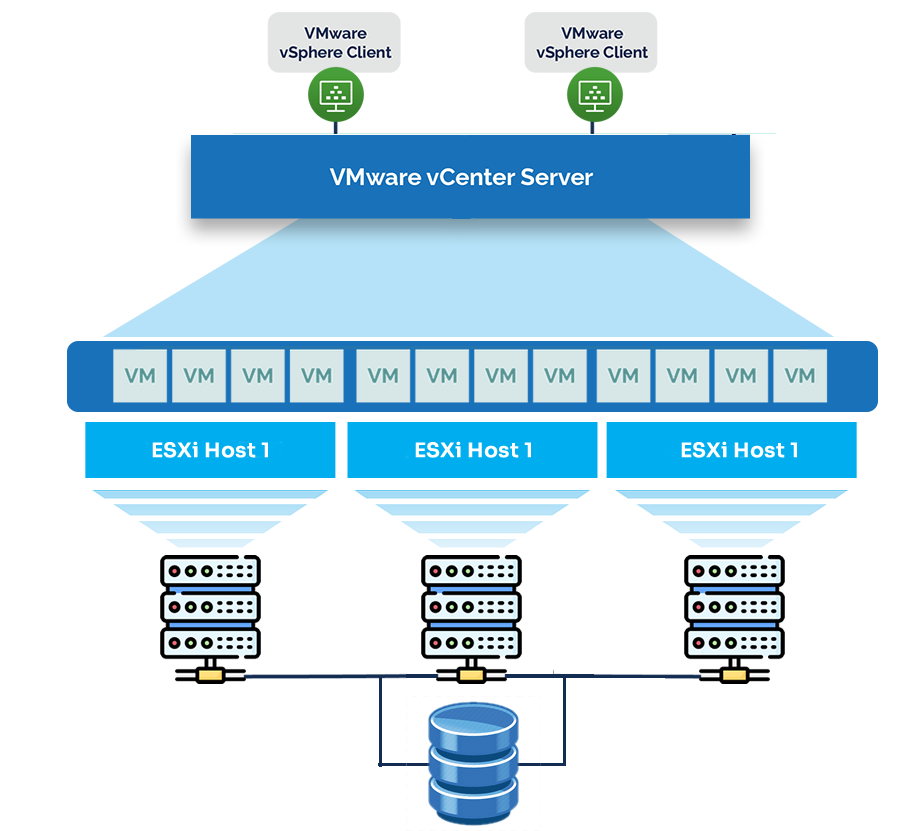
1. VMware ESXi: The Foundation of Virtualization
VMware ESXi is the core hypervisor that enables virtualization. It’s a bare-metal hypervisor, meaning it installs directly onto the physical server without requiring a host operating system. ESXi abstracts the server’s CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources, allowing you to create and run VMs.
Backtracking a little, there are two types of hypervisors, type 1 and type 2. In summary, type 1 hypervisors sits directly on top of the bare metal server (Bare metal is a name used to describe servers that have no OS installed on them yet) and has direct access to the hardware resources. Because of this, the type 1 hypervisor is also known as a bare metal hypervisor. However, type 2 hypervisors are installed on the host operating system of a machine; an example is VMware Workstation.
Features of ESXi:
- Lightweight and Efficient: ESXi has a small footprint, ensuring maximum resources are available for VMs.
- High Performance: Optimized for running multiple VMs simultaneously with minimal overhead.
- Secure: Built-in security features like secure boot and encryption protect your VMs and data.
ESXi is the foundation of your virtual infrastructure. Once installed on a physical server, it allows you to create and manage VMs directly through the ESXi host interface. However, for larger environments, managing multiple ESXi hosts individually can become very difficult. To solve this, enter vCenter Server!
2. vCenter Server: Centralized Management
vCenter Server is the centralized management platform for VMware environments. It is like a control center, allowing you to manage multiple ESXi hosts and the VMs on these hosts, from a single pane of glass (or an interface). With vCenter Server, you can streamline operations, automate tasks, and gain deeper insights into your infrastructure.
Features of vCenter Server:
- Unified Management: Manage all your ESXi hosts and VMs from a single console.
- Resource Optimization: Allocate resources dynamically to ensure optimal performance.
- Automation: Automate routine tasks like VM provisioning, patching, and backups.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Gain visibility into performance, usage, and health of your infrastructure.
In summary, if you use multiple ESXi hosts, vCenter Server is a no-brainer for easy management. Vcenter makes management simple, improves efficiency, and enables advanced features like vMotion (live VM migration, a very cool feature) and High Availability (HA).
3. vSphere: The Complete Virtualization Platform
vSphere is a platform that encompasses both ESXi and vCenter Server, along with additional tools and features. I like to think of vSphere as the umbrella for VMware’s virtualization ecosystem. It provides everything you need to build, manage, and optimize a virtual infrastructure.
Features of vSphere:
- Scalability: Support for thousands of VMs and hosts, making it ideal for enterprises of all sizes.
- Advanced Capabilities: Features like Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), Storage vMotion, and Fault Tolerance (FT) enhance performance and reliability.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other VMware products and third-party solutions.
vSphere is designed to meet the needs of modern data centers, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and resilience.
How These three Components Work Together
Now that we’ve covered the individual components, let’s see how they work together to create a cohesive virtual infrastructure:
- ESXi Hosts: These are the physical servers running the ESXi hypervisor. Each host can run multiple VMs, sharing its resources among them.
- vCenter Server: This central management platform connects to all your ESXi hosts, allowing you to manage them as a single entity. You can monitor performance, allocate resources, and automate tasks across the entire infrastructure.
- vSphere: This is the overarching platform that ties everything together. It provides the tools and features needed to optimize and scale your virtual environment.
Imagine you have five ESXi hosts running 50 VMs. Without vCenter Server, you’d need to manage each host individually. With vCenter Server and vSphere, you can:
- Monitor the health and performance of all hosts and VMs from a single dashboard.
- Use vMotion to migrate VMs between hosts without downtime.
- Implement DRS to automatically balance workloads across hosts for optimal performance.
Benefits of VMware Virtualization for Organizations
Using VMware to implement virtual infrastructure offers great benefits:
- Hardware Efficiency: By consolidating multiple workloads onto a single physical server, you can significantly reduce hardware costs.
- Scalability: Horizontally scale by adding new VMs or vertically by adding hosts as your needs grow, without disrupting existing operations.
- Disaster Recovery: Features like vSphere Replication and HA ensure business continuity in the event of hardware failures.
- Simplified Management: Centralized management through vCenter Server reduces the complexity of managing large environments.
- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware, energy, and maintenance costs lead to a lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
Setting Up Your VMware Virtual Infrastructure
Here’s a high-level overview of the steps to set up a VMware virtual infrastructure:
- Plan Your Infrastructure: Assess your organization’s needs, including the number of VMs, storage requirements, and network configuration.
- Install ESXi: Download and install ESXi on your physical servers.
- Set Up vCenter Server: Install and configure vCenter Server to manage your ESXi hosts.
- Create and Manage VMs: Use vCenter Server to create, configure, and manage your VMs.
- Optimize with vSphere: Implement advanced features like DRS, HA, and vMotion etc.
Final Thoughts
VMware’s virtualization solutions—ESXi, vCenter Server, and vSphere—provide a powerful and flexible platform for building and managing virtual infrastructures. By consolidating workloads, improving hardware efficiency, and simplifying management, VMware helps organizations achieve their IT goals while reducing costs.
In my next article, I will be setting up a Virtual Infrastructure using Vmware. I will be configuring ESXi, vSphere and vCenter, integrating with Active Directory. I will also explore managing storage, DRS, vMotion, High Availability and Fault Tolerance.


